Querying - Standard Query Form
Standard Query Form
| Create a query | How do I search for more than one term? | |
| Create a subentry query | How do I search for a phrase? | |
| How do I select a search field? | ||
| How do I control how my search terms are combined? |
More about the Standard Query Form.
Standard Query Form - Tasks
Create a Query
Before using the query form you must already have selected the databanks you want to search.
- From the first drop-down list of fields, select the field you want to search.
- Type your search term in the text box beside the selected field.
- Repeat the above steps for any further search terms.
- Turn Use wildcards off if preferred.
- Set Combine search terms with to the appropriate value.
- Specify the Number of entries to display per page.
- Choose a view using the Use view drop-down list or create your own view using the Create your own view options. (See chapter 5, "Views", for information on defining a view.)
- Set Get results of type to the required type. This is particularly useful for subentry searches.
- Click the
 button. Your results will be displayed using the selected view.
button. Your results will be displayed using the selected view.
Note:You can search up to 4 different data fields at a time using this form. You can also use Boolean operators within a single field to combine search terms and create more advanced searches.
Tip:To find out more information about a data field, click the ![]() icon beside it.
icon beside it.
Tip:To use subentries in your search, choose one or more datafields of subentry type.
Standard Query Form - Worked Examples
Create a Query
This example demonstrates a search of the EMBL databank for entries having amylase in the description field and bacillus sp in the organism field that have been updated since Jan 1st 2000. They will be viewed using the default view.
If you have not already done so, go to the Select Databanks To Search page (Select Databanks tab) and select the EMBL databank.
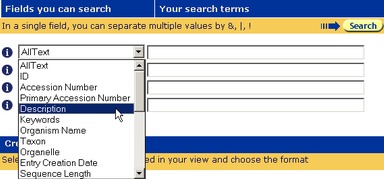
- From the first drop-down list of fields, select the Description field.
- Type amylase in the text box beside Description.
- Repeat the above steps in the second row, setting the field to Organism Name and typing bacillus sp in the text box beside it.
- In the third row, set the field to LastUpdated.
- In the text box beside that, type -JAN-2002:, noting that the colon after the date tells SRS to look for dates after that one. Without the colon SRS will look for entries that were updated on that date exactly.
- Ensure that combine searches with is set to & (AND).
- Click the
 button. Your results will be displayed using the selected view.
button. Your results will be displayed using the selected view.
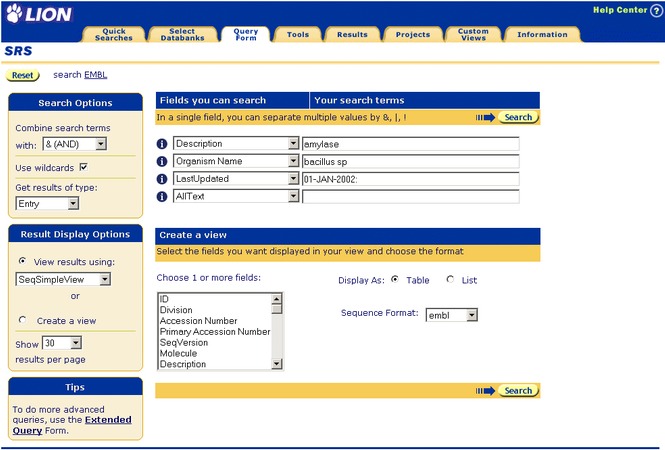
Figure 3.1 Standard Query Form showing a query for EMBL for entries containing the word, amylase, in the Description field, with bacillus sp in the Organism Name field that were added to the databank after January 1, 2002.
Create a Subentry Query
Searching for Entries which Reference Papers that include those by Smith and by Jones
In this example entries will be retrieved from SWISS-PROT that reference papers by Smith and Jones. For an entry to be retrieved there must be papers whose authors include Smith and Jones, but Smith and Jones need not be co-authors of the same paper.
If you have not already done so, go to the Select Databanks To Search page and select the databank you wish to search, e.g. SWISS-PROT.
- Use the first drop-down datafield list to select the subentry field, Reference:Authors.
- Enter smith in the first text box, beside where you selected Reference:Authors. The search is case insensitive, so it does not matter whether smith is written with a lower or upper case S.
- Repeat the process for the next line of information, using the name jones rather than smith.
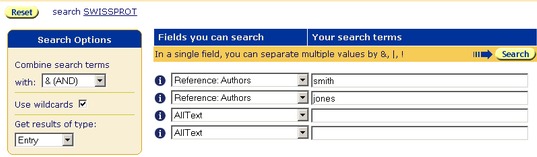
Figure 3.2 Standard Query Form showing a query for entries, using the Reference:Authors subentry fields.
- Leave combine searches with set to & (AND).
- Leave retrieve entries of type set to Entry.
- Click the
 button.
button.
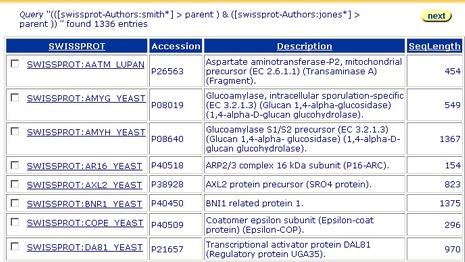
Figure 3.3 Query Result page showing the results of a query for entries, using the Reference:Authors subentry fields, using two separate text boxes to search on the Standard Query Form.Tip:Using two separate text boxes for the subentries search retrieves all entries containing references by Smith, and by Jones, including those where there are no papers which were co-authored by Smith and Jones. Figure 3.4 shows an entry from the above search.

Figure 3.4 Entry page showing that some entries reference only papers that are not co-authored by Smith & Jones. (SWISS-PROT accession number P46161.)Tip:In effect, this search looks for reference subentries that contain smith or jones. It then takes the entries for each of the references matching the criteria, to create two lists of entries: one for smith and one for jones. It then combines those, seeking only those which are in both lists.
Searching for Entries which Reference Papers that are Co-authored by Smith & Jones
In the above example, entries were retrieved that referenced papers by Smith and Jones, but without concern for whether Smith & Jones were co-authors of any papers.
If you wish to search for entries that reference papers that are always co-authored by Smith & Jones, you should modify your search, so that rather than searching in two separate text boxes on the Standard Query Form, you search for both authors in a single text box.
If you have not already done so go to the Select Databanks To Search page and select the databank you wish to search, e.g. SWISS-PROT.
- Use the first drop-down datafield list to select the subentry field, Reference:Authors.
- In the text box beside the datafield you have used, type smith & jones.
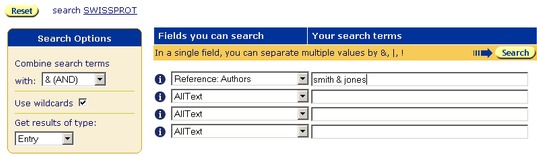
Figure 3.5 Standard Query Form showing a query for entries, using the Reference:Authors subentry fields, searching for papers which are co-authored by Smith & Jones.
- Leave combine searches with set to & (AND), and retrieve entries of type set to Entry.
- Click the
 button.
button.
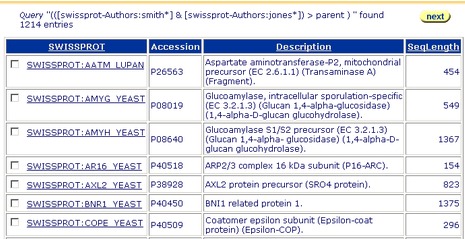
Figure 3.6 Query Result page showing the results of a query for entries, using the Reference:Authors subentry fields, using a single text box with two search terms, to search on the Standard Query Form.Note:In effect, this search looks for reference subentries that contain smith or jones. It then combines these to create a list of those that contain both Smith and Jones in a single reference subentry. It then takes the entries for each of the references matching the criteria. This creates a single list of entries, which contain references to papers which are co-authored by Smith and Jones.
Searching for Subentries which Reference Papers that are Co-authored by Smith & Jones
If you wish to retrieve the subentry fields that are found, rather than the parent entries, the searches can be repeated with the retrieve entries of type set to Reference.
- Repeat one of the above searches, but set retrieve entries of type to Reference.
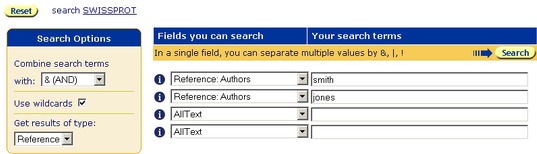
Figure 3.7 Standard Query Form showing a query for subentries, using the Reference:Authors fields.Note:This search will retrieve the subentries that match the criteria rather than the parent entries. Otherwise, the search behaves similarly to the above, so that searching for the two terms in a single text box, combined with & will produce reference subentries that contain only co-authored papers, whilst searching for the two terms using separate text boxes will produce reference subentries which contain papers by both authors, but will not check whether they are co-authors.
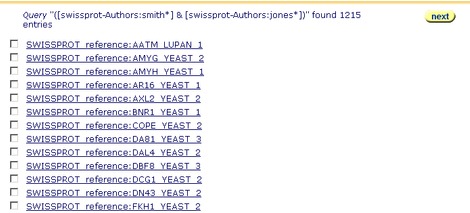
Figure 3.8 Query Result page showing the results of a query for subentries, using the Reference:Authors subentry fields, using the Standard Query Form.
Standard Query Form - FAQs
Search for More Than One Term
Use subsequent rows of the table to choose further datafields (which may be the same as the first) and enter your search terms beside them.
Alternatively, if you want to search for more than one thing within any particular field, you can use the boolean operators (&, |, !) to combine two or more entries within a given text box. This is particularly useful for subentries.
Search for a Phrase
Enter your phrase within a single text box.
Select a Search Field
- Locate the search field you want to use in the drop-down list.
- Click on the required field.
How Do I Define How My Search Terms are Combined?
Use the Boolean operators in the combine searches with drop-down list to combine terms in separate rows.
Alternatively, type them into the text boxes between your search terms. The available operators are:
| & | AND | phosphorylase & methyltransferase |
| | | OR | rat | mouse |
| ! | BUTNOT | nitrogenase ! reductase |
Multiple terms can be combined using brackets, e.g. to search for entries whose Organism Name field contains rat or mouse, but not bovine, you could type:
(rat | mouse) ! bovine
Standard Query Form - Reference

Figure 3.9 Standard Query Form.
Getting to the Standard Query Form
This page can be reached by any of the following methods:
- Clicking the Query tab (unless the default Query Form has been changed, see "Make Default Query Page", p. 27).
-
Clicking the
 button on the Select Databanks To Search page.
button on the Select Databanks To Search page. - Clicking on the Standard Query form link on an Extended Query Form page.
Using the Standard Query Form - Options Area
Search ...

Submit Query
Click the  button once a query has been defined. The results of the query will be displayed on a Query Result page (see section 3.5 "Query Result Page", p. 41).
button once a query has been defined. The results of the query will be displayed on a Query Result page (see section 3.5 "Query Result Page", p. 41).
Use Wildcards
By default this box is ticked and wildcards are appended to all search words automatically. If wildcards are not to be appended, untick the check box.
Combine Searches With
The query terms will have a relationship with each other that is either inclusive or exclusive. Using the drop-down list you can choose the way your search terms are combined.
- & (AND)
- All the query terms must be present for an entry to be included in the results of the query. This is the default.
- | (OR)
- If any of the terms are present in an entry it will be included in the results.
- ! (BUTNOT)
- The first term must be present but the other terms must be absent from the entry for it to be included in the results.
Number of Entries to Display per Page
This drop-down list allows you to specify the maximum number of entries to be listed per page of results. When the number of entries is greater than this value, entries will be spread over two or more pages.
Extended
The Extended Query form link displays the Extended Query Form. This allows a query to be continued using the Extended Query Form without having to reselect the databank(s).
Make Default Query Page
This option does not usually appear unless the Extended Query Form has been set as the default. The check box can be ticked to make the Standard Query Form into the default used for queries. Making this the default Query Form means that if the Query tab is clicked, the Standard Query Form is used, rather than the Extended Query Form. A query must be submitted for this to take effect.
Using the Standard Query Form - Data Area
Submit Query
Click one of the  buttons once a query has been defined. The results of the query will be displayed on a Query Result page.
buttons once a query has been defined. The results of the query will be displayed on a Query Result page.
Field Information
Clicking on one of the ![]() icons beside a datafield in one of the drop-down lists will display the Field Information page (see section 7.3 "Field Information Page", p. 105) for the currently selected field.
icons beside a datafield in one of the drop-down lists will display the Field Information page (see section 7.3 "Field Information Page", p. 105) for the currently selected field.
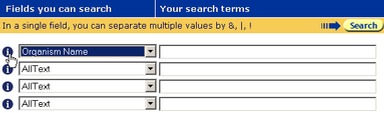
Datafield
The upper left-hand side of the Data Area contains drop-down lists. These allow a datafield to be selected for searching, from a list of those available for the current query. There are four such lists, allowing a query to use up to four datafields.
Search Text
The upper right-hand side of the Data Area contains text boxes in which a search term can be entered. It is possible to search for more than one term in each text box, using the operators, & (AND), | (OR) and ! (BUTNOT), to indicate how the terms should be related. There are four such text boxes, allowing a query to use up to four datafields.
Retrieve Entries of Type
This option allows you to choose whether to retrieve entire entries or subentries, such as references, features or counters. It is useful when searching subentries. See also "Subentries" in chapter 3, "Querying with SRS", of the SRS User Guide.
View Results Using
A predefined view can be used to display the results of a search. This is chosen using the drop-down list, which contains the built-in views, and any views created during the current project (see section 5.1 "View Manager Page 1", p. 70).
Create Your Own View
If none of the predefined views shows everything that is required, it is possible to specify the datafields to be used to display the results of the current query.
You can choose whether you want the view to be a table or list view, by selecting the required option. The default is a table view.
The sequence format can also be specified.
The view is created when the query is performed, i.e. when one of the  buttons is clicked.
buttons is clicked.
Note:This custom view is not saved and is only available for the query with which it was created.
Other Information
